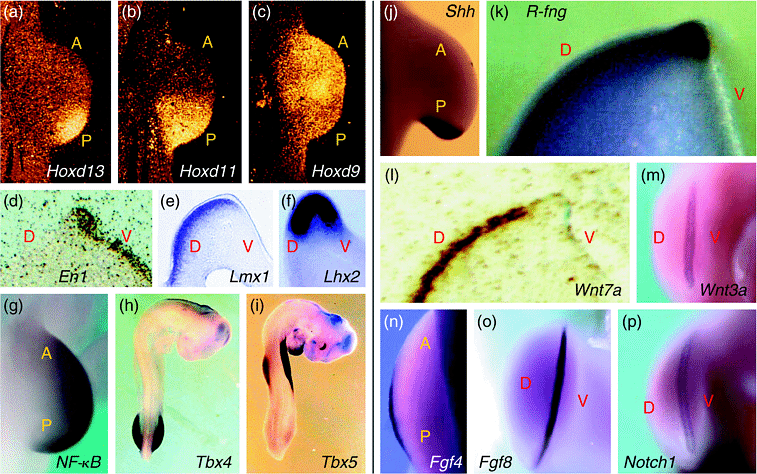
Рис. 2 Wnt7a и Lmx1 экспрессия ограничена дорсальной эктодермой и мезодермой, соответственно, тогда как En1 локализуется в вентральной эктодерме. R-fng экспрессия первоначально ограничена дорсальной эктодермой, позднее обнаруживается в AER. Fgf8, Notch1 и Wnt3a экспрессируются во всем AER, а Fgf4 локализуется в задней части AER. NF-κB и Lhx2 располагаются в подлежащей мезенхиме или прогрессивной зоне. Наиболее posterior члены Hoxd (в данном случае Hoxd9, -11 и -13) комплекса обнаруживают гнездовый паттерн экспрессии вдоль переднезадней оси, центр которой находится в зоне поляризующей активности, которой ограничиваются транскрипты Shh. Tbx5 и -4 экспрессируются в передних и задних конечностях соответственно.
Figure 2. Gene-expression patterns of various transcription factors and signalling molecules during limb budding. The figure is divided such that on the left side some of the transcription factors and, on the right side, some of the signalling molecules shown to have a role during limb development, are displayed. Wnt7a and Lmx1 expression is restricted to the dorsal ectoderm and mesoderm, respectively, while En1 is localized to the ventral ectoderm. R-fng expression, initially restricted to the dorsal ectoderm, is later on localized to the apical ectodermal ridge (AER). Fgf8, Notch1 and Wnt3a are expressed throughout the entire AER, and Fgf4 is localized to the posterior AER. NF-κB and Lhx2 are localized in the underlying mesenchyme or progress zone. The most posterior members of Hoxd (in this case Hoxd9, -11 and -13) complex display a nested pattern of expression along the anteroposterior limb axis, centred at the zone of polarizing activity where transcripts for Shh are restricted. Tbx5 and -4 are expressed in fore- and hind-limb, respectively. These genes are members of the T family of genes and could be involved in specifying fore- versus hind-limb identity. (Courtesy K.W. Tosney, Univ. of Michigan, USA.)
Сайт создан в системе
uCoz