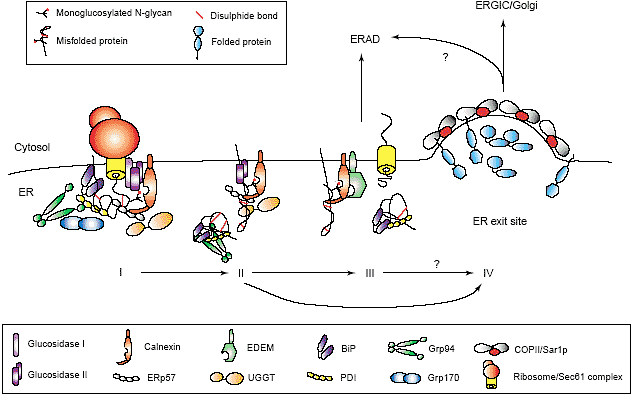Если после высвобождения от хаперонов секреторный белок укладывается корректно, то он д. покинуть ER, возможно с помощью lectin
ERGIC-53, если он является гликопротеином [35]. Если, с др. стороны, белок не м. уложиться, даже после продолжительного времени, то он д.б. удален с конвеера укладки и отправлен на ER-ассоциированную деградацию (ERAD). Путь ERAD ретро-транслоцирует (dislocates) неправильно упакованный белок обратно в цитозоль, где происходит деградация с помощью протеосом.
На дрожжах было продемонстрировано, что и BiP и PDI участвуют в ERAD. BiP м. удерживать неправильно упакованные белки в обратимо агрегированном состоянии, тогда как PDI непосредственно направляет неправильно упакованные белки на retrotranslocation [53].
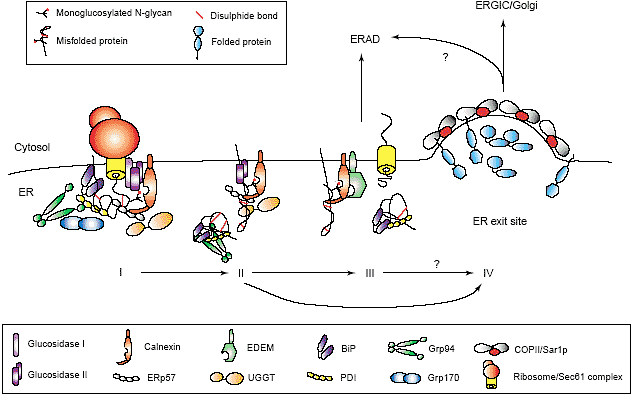 QC by BiP- and CNX-containing complexes follows successive steps. BiP and CNX with their accessory proteins associate with nascent chains as soon as they enter the ER lumen (I), and continue to assist folding after translation (II). When the protein has acquired its correctly folded structure, it is ready for exit from the ER (IV). If the protein fails to reach its native state the chaperones and folding enzymes target and guide the misfolded protein for ERAD (III). For at least some proteins, ER to Golgi traffic is necessary before ERAD, probably via COPII exit sites (IV).
QC by BiP- and CNX-containing complexes follows successive steps. BiP and CNX with their accessory proteins associate with nascent chains as soon as they enter the ER lumen (I), and continue to assist folding after translation (II). When the protein has acquired its correctly folded structure, it is ready for exit from the ER (IV). If the protein fails to reach its native state the chaperones and folding enzymes target and guide the misfolded protein for ERAD (III). For at least some proteins, ER to Golgi traffic is necessary before ERAD, probably via COPII exit sites (IV).
Установлено, что Ero1 обеспечивает высвобождение не упакованного холерного токсина, связанного с PDI до retrotranslocation [54]. В др. исследовании смешанные дисульфидные связи были обнаружены между PDI и мембранным гликопротеином BACE457 до ERAD [55]. Напротив, PDI также обнаруживает связь с субстратом redox-независимо [56]. Если укладка гликопротеина не удается, то α-mannosidase I д. отрезать одну mannose, это д. направлять белок на деградацию с помощью EDEM, другого lectin [57]. CNX взаимодействует посредством своего трансмембранного домена с EDEM, чтобы передать неправильно упакованный α1-antitrypsin b BACE457 [58,59]. Взаимодействие CNX/EDEM поддерживает важную передачу от хаперона к ERAD. Т.к. CRT не м. соединяться с EDEM, то будут обнаружены скорее всего многие lectins.
Более того, детальный анализ композиции олигосахаридов из EDEM-связанного субстрата, показал, что дополнительные гликоформы подготавливают белок для ERAD. Как BiP так и lectin хапероны участвуют в отсылке неправильно упакованных белков на ERAD. Т.к. неправильно упакованный BACE457 является субстратом для PDI и EDEMit, то остается неясным, оба ли хаперона или их ко-факторы и redox энзимы сотрудничают для достижения этой цели. Т.к. ERp57 сильно напоминает PDI, этот private redox партнер для CNX, то он м. также вызывать редукцию собственных дисульфидных связей для retrotranslocation.
Conclusions
The question remains of how the ER decides at the
molecular level between the protein folding and ERAD
pathways (Figure 1). The kinetics of the folding and
degradation pathways may simply differ, as glucosidase
activity is suggested to be higher than mannosidase
activity. This may favour the folding cycle over ERAD
[60]. After multiple rounds of chaperone binding, proteins
that inefficiently fold are eventually targeted for degradation.
On the other hand, protein folding might be spatially
separated from protein degradation by distinct ER subdomains.
Two ERAD substrates, asialoglycoprotein
receptor H2a and unassembled MHC class I, accumulated
before ERAD in ER subcompartments that colocalised
with Sec61, CNX and CRT but not with BiP and
PDI [61,62]. Genetic evidence in yeast suggests that the
Sar1p/COPII machinery is essential in proteasomal sorting
[63]. These various observations narrow down the
location of the decisions to the ER exit site (reviewed by
Watanabe and Riezman in this issue), which then would
be involved in the triad decision between protein folding,
protein degradation and protein export. Flexible protein
complexes are likely to be at the molecular core of this
fate-determining process. Exactly how these folding factor
complexes work in mammalian cells can now be
addressed using siRNA. Folding factors can be
knocked-down one by one to study the effect on the
complete folding factor network and hence on protein
folding and quality control.
Update
Co-translational folding has received increasing appreciation
over the last years. Two recent studies by Woolhead
et al. and Gilbert et al. put focus on the ribosome in
relation to folding. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer
(FRET) showed folding (increasing compactness) of a
transmembrane segment inside the ribosomal tunnel
[64�]. Comparing density maps of Cryo-EM on translating
versus non-translating ribosomes demonstrated occlusion
inside the tunnel when ribosome is engaged in protein
synthesis of Ig1, Ig2, or GFP [65]. Both laboratories
present compelling evidence that newly synthesised proteins
may begin to fold inside the ribosome.
Сайт создан в системе
uCoz