Посещений: 
НАСЛЕДСТВЕННЫЕ БОЛЕЗНИ СЕТЧАТКИ
Генетический контроль
Identification and Analysis of Genes Associated with Inherited Retinal Diseases • Mubeen Khan
• Zeinab Fadaie
• Stephanie S. Cornelis et al.
 Retinal Degeneration pp 3-27 Part of the Methods in Molecular Biology book series (MIMB, volume 1834)
| |
|
1.1 Spectrum of Inherited Retinal Diseases
Inherited retinal diseases (IRDs) представляет клинически и генетически гетерогенную группу нарушений, затрагивающих сетчатку. Эти болезни классифицируются на базе преимущественных нарушений палочек (напр., retinitis pigmentosa , RP) или колбочек (напр., cone and cone-rod dystrophies, CD/CRD) или вызываются более генерализованными заболеваниями фоторецепторов (напр., Leber congenital amaurosis , LCA) [1]. Большинство IRDs ассоциируютс с постепенным изнашиванием в теченрие жизни, тогда как некоторые из них не прогрессирующими (напр., congenital stationary night blindness , achromatopsia , некоторые формы LCA). Дифференциальная диагностика между разными IRDs может иногда осложняться, поскольку клинические проявления некоторых IRDs могут быть очень сходными, как на ранней, так и поздней стадии. (Fig. 1).
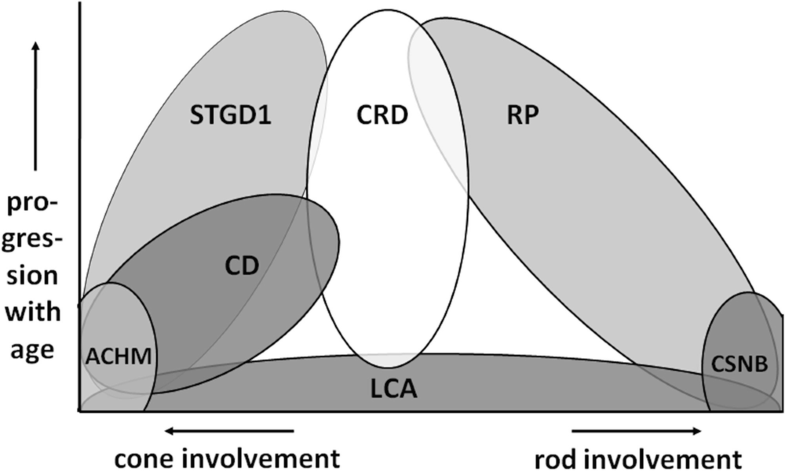 Fig. 1
Fig. 1
Phenotypic overlap between autosomal recessive retinal diseases. Patients with achromatopsia (ACHM) display a virtually stationary disease course in which cones are principally defective. At end stages, cone dystrophy (CD) can hardly be distinguished from cone-rod dystrophy (CRD). Patients with Stargardt disease (STGD1) later in life show mid-peripheral defects similar to CRD patients . Patients with retinitis pigmentosa (RP) initially display night blindness, followed by tunnel vision due to rod defects which very often progresses to complete blindness when the cones are also afflicted. In patients with Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA), the defects can occur in both types of photoreceptors, or in M?ller or RPE cells, and therefore both clinical and molecular genetic overlap with CD, CRD, or RP can be expected. Patients with congenital stationary night blindness (CSNB) show a rod-specific defect IRDs могут наследоваться аутосмно рецессивно, аутосомно доминантно и Х-сцепленным способом (Fig. 2). Для отдельных случаев мужчин и женщин с RP (Fig. 2b, c, h, i), наблюдаются все способы наследования, это частично объяснеяется наблюдением, что de novo мутации вносят существенный вклад в доминантные не семейные заболевания [2, 3].
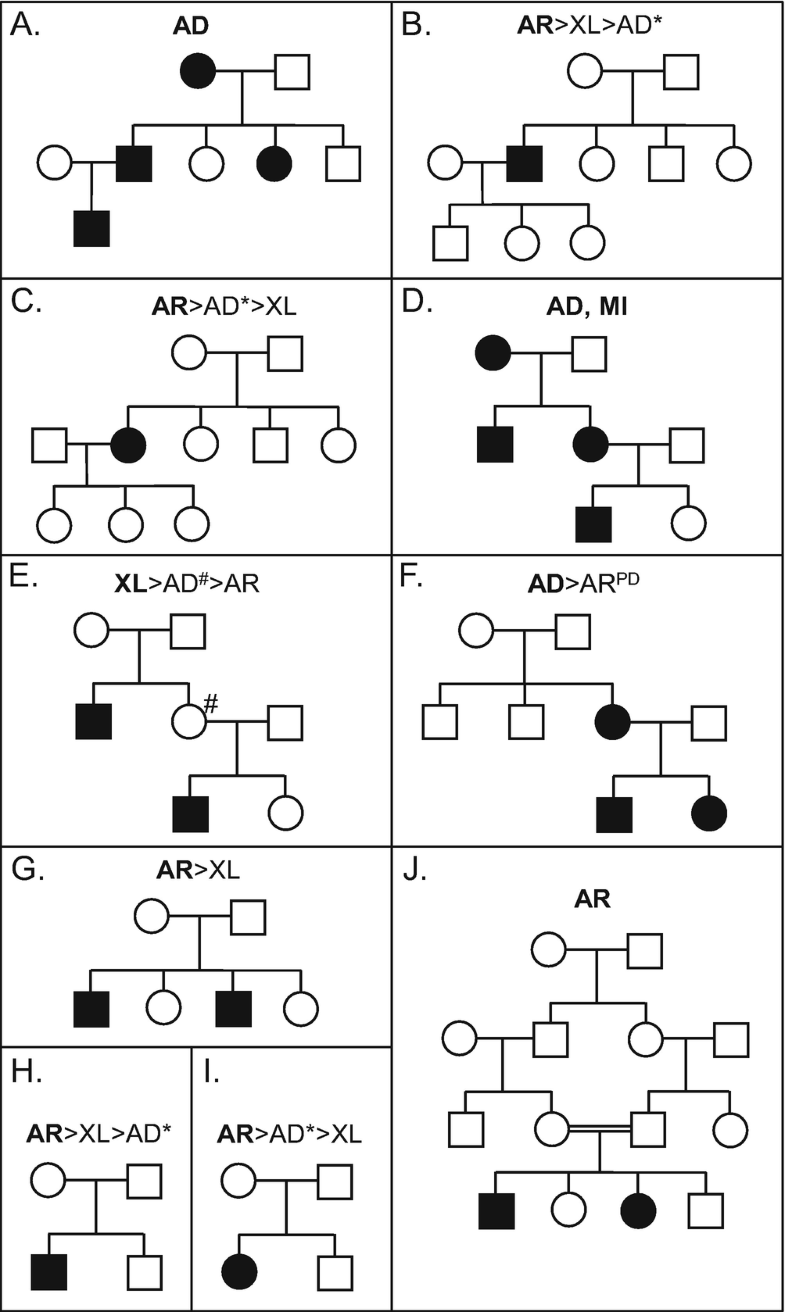 Fig. 2 Fig. 2
Examples of the different modes of inheritance observed in retinal diseases. Illustration of inheritance models based on the occurrence and gender of affected individuals and their position in the pedigree. In bold above the pedigrees, the most likely modes of inheritance are given, followed by the less likely modes of inheritance. AD autosomal dominant , AR autosomal recessive , MI mitochondrial inheritance, PD pseudodominant (autosomal recessive) inheritance, XL X-linked recessive , *de novo mutation, #non-penetrant individual Хотя некоторые болезни вызываются мутациями в довольно небольшом количестве генов, наиболее часто встречающиеся IRDs являются генетически высоко гетерогенными со многими причинными генами (Fig. 3). Крайним случаем является RP , который на сегодня ассоциирован с мутациями в 84 разных генах. Кстати, мутации в 261 гене были идентифицированы у пациентов с несиндромальными и синдромальными IRDs, было подсчитано, что эти гены объясняют ~80% от генетического груза болезней [4, 5]. Т.к. большинство недавно идентифицированных генетических дефектов при IRDs найдено в единичном случае или семье, то трудно предсказать сколько IRD-ассоциированных генов ещё будет идентифицировано. Все известные IRD-ассоциированные гены и соотв. способ наследования представлены в базе данных http://www.sph.uth.tmc.edu/RetNet/.
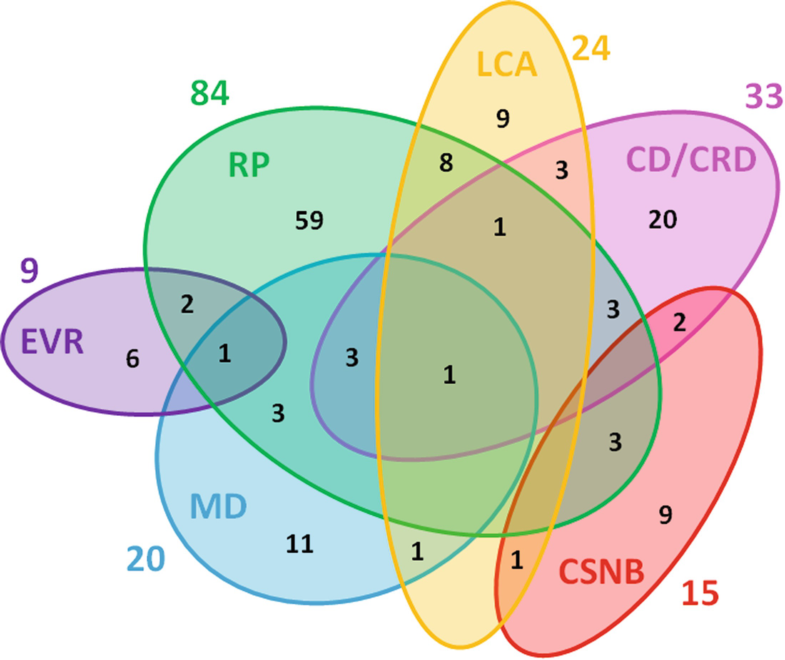 Fig. 3 Fig. 3
Genetic overlap between non-syndromic monogenic retinal diseases. Clinical diagnoses are indicated by colored circles. In the overlapping areas, we provide the number of genes implicated in different phenotypes . Colored numbers outside the balloons represent the total number of genes associated with these phenotypes. RP retinitis pigmentosa , CSNB congenital stationary night blindness , LCA Leber congenital amaurosis , CD/CRD cone and cone-rod dystrophies, MD macular degeneration, EVR exudative vitreo retinopathies
|
 Fig. 1
Fig. 1 Fig. 2
Fig. 2  Fig. 3
Fig. 3