Посещений: 
Нарушения двигательных нейронов (Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) и spinal muscular atrophies (SMAs))
Задание предварительных условий для увеличения жизнеспособности нейронов
Preconditioning and Cellular Engineering to Increase the Survival of Transplanted Neural Stem Cells for Motor Neuron Disease Therapy • Elena Abati
• Nereo Bresolin
• Giacomo Pietro Comi
• Stefania Corti
 Molecular Neurobiology
May 2019, Volume 56, Issue 5, pp 3356-3367|
| |
|
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) и spinal muscular atrophies (SMAs) являются тяжелыми болезнями, характеризующимися избирательной дегенерацией двигательных нейронов. ALS является неизлечимой, прогрессирующей нейродегенеративной болезнью, характеризующейся потерей верхних и нижних двигательных нейронов, что приводит к необратимым мышечным параличам и в конечном итоге к респираторной недостаточности и гибели в теч6ении 3 - 5 лет после начала [1]. Кстати, существуют только два разрешенных метода терапии, riluzole и edaravone, с минимальным влиянием на жизнеспособность, доступных для лечения ALS, вместе с поддерживающим уходом (e.g., neurorehabilitation) [2, 3]. SMAs являются наследственными дегенеративными нарушениями, затрагивающими двигательные нейроны передних рогов серого вещества спинного мозга. Proximal 5q SMA возникает в результате гомозиготных мутаций в гене survival motor neuron 1 (SMN1). Nusinersen, антисмысловой олигонуклеотид, модулирующий экспрессию SMN2, был недавно одобрен в качестве терапии первой линии дляr SMA 5q. Однако, отсутствует доступное лечение для др. типов SMA [4].
Несморя на разнообразные исследования в этой области, на сегодня отсутствуют имеющие силу терапевтические стратегии, способные ротивостоять потере нейронов после их возникновения и регенерировать поврежденную ЦНС. Более того, сложный динамический процесс, лежащий в основе патогенеза motor neuron diseases (MNDs) и относительно избирательная гибель двигательных нейронов остается неуловимым. Поэтому существует настоятельная потребность пролить свет на участвующие клеточные и молекулярные сети, чтобы идентифицировать новые мишени лля разработки лекарств и неотразимые терапевтические подходы. Очевидно, что пригодная к MNDs, регенеративная терапия д. в конечном счете регулировать gkg противодействовать этим сложным путям, способствуя тем самым поддержанию или восстановленияю функции моторных нейронов [5].
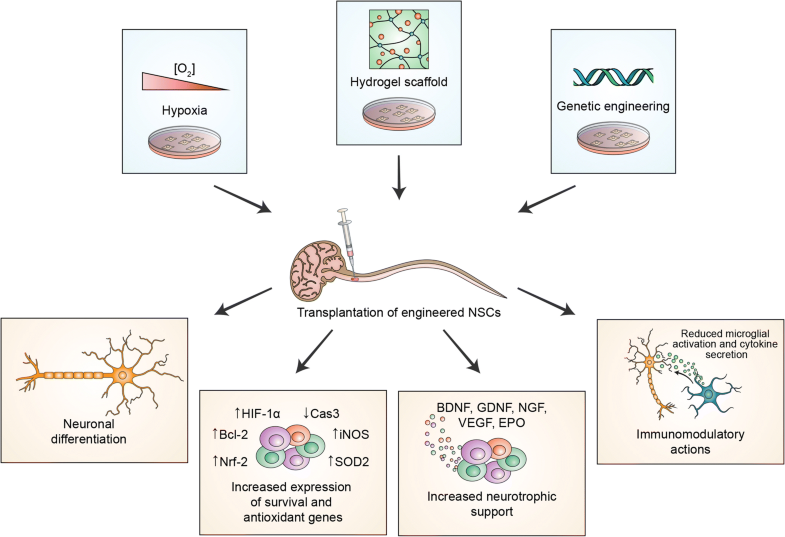
Fig. 1
Engineering strategies to increase stem cell engraftment and survival within the host tissue include hypoxic and pharmacological (minocycline, adjudin, interleukin-6, BDNF) preconditioning, seeding of cells into biomaterial scaffolds, and genetic manipulation to overexpress neurotrophic or survival genes. When transplanted into the CNS, treated cells show reduced death rates and increased proliferative abilities. Furthermore, they display enhanced neuroprotective properties, increasing endogenous neuroblasts proliferation and migration and reducing infarct size and reperfusion-induced injury in experimental models. In addition to that, engineered cells appear able to increase expression of anti-apoptotic (HIF1a, Bcl-2), antioxidant (iNOS, SOD2, catalase, Nrf2), and trophic (VEGF, EPOR) genes. Remarkably, they can also promote the secretion of neurotrophic factors (GDNF, BDNF, VEGF, NGF, NT-3) and reduce cytokine production and microglial activation
Трансплантационные подходы, базирующиеся на экзогенных нейральных стволовых клетках, были исследованы в качестве многосторонних стратегий для защиты и репарации верхних и нижних двигательных нейронов от дегенерации и воспаления. Трансплантируемые нейральные стволовые клетки (NSCs) оказывают свои благоприятные эффекты не только благодаря замещению поврежденных клеток, но и также благодаря соотв. иммуномодулирующим и нейротрофным действиям. Несмотря на это такие многообещающие находки, перенос в клинику такой техники подвержен опасности из-за ограниченного успеха в приживлении и жизнеспособности трансплантированных клеток внутри враждебного микроокружения при болезни. Для преодоления этих обстоятельств и усиления жизнеспособности, стабильности и терапевтического потенциала трансплантатов были разработаны более продвинутые методы, включая средовые стрессы, для создания заданных предварителных условий, биополимерные поддержки и генетические преобразования. В обзоре обсуждаются современные техники преобразований, имеющие целью использовать миграторную, пролиферативную и секретируемую способности NSCs и определить их значение для терапевтического арсенала против нарушений двигательных нейронов и др. нейрологических нарушений.
Table 1
Hypoxic preconditioning of NSCs prior to transplantation in the CNS
Cell source and treatment Experimental model Transplantation Outcomes Ref.
Mouse ESC-derived NPCs exposed to 1% O2 for 8 h Rat tMCAO (120 min) 48 h after MCAO; intracerebral 30-40% reduced cell death after transplantation.
Greater improvement in sensorimotor functions compared to the non-preconditioned group.
↑ expression of Bcl-2, NF, synaptophysin, HIF1alpha.
↑ EPO secretion. [79]
Primary rat BMSCs exposed to 0.5% O2 for 24h Rat tMCAO (90 min) 24 h after MCAO; intravenous ↑ survival of NSCs.
Greater improvement in brain functional recovery and motor
functions compared to the non-preconditioned group.
↑ expression of GDNF, BDNF, VEGF, VEGF receptor Flk-1 and angiotensin-1.
↑ expression of chemokine SDF-1 and CXCR4.
↑ EPO secretion and EPOR expression. [80]
Primary rat BMSCs exposed to 0.1-0.3% O2for 24 h Mouse, experimental ICH induced with collagenase IV 72 h or 7 days after ICH; intranasal
↑ perilesional levels of BDNF, GDNF, and VEGF.
↑ neuroblast proliferation and migration.
Improved functional recovery.
↑ brain atrophy changes. [81]
Mouse iPSC-derived NPCs exposed to 0.1-0.3% O2for 8 h Rat, stereotaxic TBI 72 h after TBI; intracerebral Improved sensorimotor outcome and social behaviors.
↑ expression of oxytocin and oxytocin receptor. [82]
Primary mouse NSCs exposed to 5% O2 for 24 h Mouse, experimental ICH induced with autologous whole blood 72 h after ICH; intracerebral
↑ survival of grafted NSCs.
Improved functional recovery.
↑ expression of HIF1alpha, phosphor-Akt, and VEGF. [33]
Primary rat NSCs exposed to 1% O2 for 2, 4 or 6 h Rat, stereotaxic SCI During procedure; intraspinal, in situ
↑ locomotor recovery.
↑ neuronal survival and reduced glial scar formation.
↑ expression of GDNF, BDNF, NT-3, and HIF1alpha. [53]
Abbreviations: BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; BMSCs, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; EPO, erythropoietin; EPOR, erythropoietin receptor; ESCs, embryonic stem cells; GDNF, glial-derived neurotrophic factor; ICH, intracerebral hemorrhage; iPSCs, induced pluripotent stem cells; NF, neurofilament; NPCs, neural progenitor cells; NSCs, neural stem cells; NT-3, neurotrophin-3; SCI, spinal cord injury; TBI, traumatic brain injury; tMCAO, transient middle cerebral artery occlusion; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor
Table 2
Pharmacological and small molecule-based preconditioning of NSCs prior to transplantation in the CNS
Cell source and treatment Experimental model Transplantation Outcomes Ref.
Primary rat NSCs cultured with minocycline hydrochloride (10 M) for 24 h Rat tMCAO (90 min) 6 h after MCAO; intracerebral
↑ survival and proliferative capacity of preconditioned grafted NSCs.
↑ expression of Nrf2 and Nrf2-regulated antioxidant genes.
↑ secretion of BDNF, NGF, GDNF, and VEGF.
Enhanced neuroprotection in ischemic area. [55]
Primary mouse NSCs cultured with IL-6 (20 ng/ml) for 24 h Mouse tMCAO (45 min) 6 h or 7 days after MCAO; intracerebral
↑ survival and ↑ death of grafted cells.
↑ expression of SOD2.
↑ in vitro and in vivo angiogenesis.
↑ infarct size.
Improved functional recovery (rotarod test). [56]
Human ESC-derived NSCs cultured with BDNF (100 ng/ml) for 1 h Mouse tMCAO (15 min) 72 h after MCAO; intra-arterial (carotid)
↑ NSC engraftment and survival in host brain.
Improved functional recovery (horizontal ladder test).
Enhanced neuroprotection in ischemic area.
↑ secretion of ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and VEGF. [57]
Primary mouse NSCs cultured with adjudin (5, 10, 30, or 60 ↑M) for 24 h Mouse tMCAO (120 min) 24 h after MCAO; intracerebral
↑ expression of antioxidant genes (iNOS, SOD2, catalase).
↑ secretion of neurotrophic factors (BDNF, GDNF, NGF).
↑ cytokine production and microglial activation.
↑ infarct size.
Enhanced neuroprotection and angiogenesis in ischemic area.
Improved functional recovery (rotarod test).
Reduced ischemia/reperfusion-induced blood-brain barrier leakage. [60]
Abbreviations: BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; ESCs, embryonic stem cells; GDNF, glial-derived neurotrophic factor; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; IL-6, interleukin-6; NGF, nerve growth factor; NSCs, neural stem cells; tMCAO, transient middle cerebral artery occlusion; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor
|
 Fig. 1
Engineering strategies to increase stem cell engraftment and survival within the host tissue include hypoxic and pharmacological (minocycline, adjudin, interleukin-6, BDNF) preconditioning, seeding of cells into biomaterial scaffolds, and genetic manipulation to overexpress neurotrophic or survival genes. When transplanted into the CNS, treated cells show reduced death rates and increased proliferative abilities. Furthermore, they display enhanced neuroprotective properties, increasing endogenous neuroblasts proliferation and migration and reducing infarct size and reperfusion-induced injury in experimental models. In addition to that, engineered cells appear able to increase expression of anti-apoptotic (HIF1a, Bcl-2), antioxidant (iNOS, SOD2, catalase, Nrf2), and trophic (VEGF, EPOR) genes. Remarkably, they can also promote the secretion of neurotrophic factors (GDNF, BDNF, VEGF, NGF, NT-3) and reduce cytokine production and microglial activation
Fig. 1
Engineering strategies to increase stem cell engraftment and survival within the host tissue include hypoxic and pharmacological (minocycline, adjudin, interleukin-6, BDNF) preconditioning, seeding of cells into biomaterial scaffolds, and genetic manipulation to overexpress neurotrophic or survival genes. When transplanted into the CNS, treated cells show reduced death rates and increased proliferative abilities. Furthermore, they display enhanced neuroprotective properties, increasing endogenous neuroblasts proliferation and migration and reducing infarct size and reperfusion-induced injury in experimental models. In addition to that, engineered cells appear able to increase expression of anti-apoptotic (HIF1a, Bcl-2), antioxidant (iNOS, SOD2, catalase, Nrf2), and trophic (VEGF, EPOR) genes. Remarkably, they can also promote the secretion of neurotrophic factors (GDNF, BDNF, VEGF, NGF, NT-3) and reduce cytokine production and microglial activation